Measuring Price Elasticity of Demand- Proportionate or Percentage Method
Learning Contents:
·
Introduction
to Proportionate method of Price Elasticity of Demand
·
Questions
For Practice
Proportionate or Percentage Method
It is one of the commonly used method for measuring the price elasticity of demand. In this method, the elasticity of demand is calculated as the percentage change in quantity demanded divided by the percentage change in price. The formula for calculating the elasticity of demand is given below:
Interpreting Elasticity of Demand using Percentage Elasticity of Demand
|
Case |
Description |
Degree of
elasticity |
Numerically, Ed |
|
1. |
If the calculated value is more than 1 |
More
than Unitary Elastic or Elastic Demand |
Ed>1 |
|
2. |
If the calculated value is equal to 1 |
Unitary
Elastic Demand |
Ed=1 |
|
3. |
If the calculated value is less than 1 |
Less
than Unitary Elastic Demand or Inelastic Demand |
Ed<1 |
Questions for Practice:
1.
When the price of a commodity was ₹10 per unit, its demand in the market was 50
units per day. When the price of the commodity fell to ₹ 8, the demand rose to
60 units. Here, the price elasticity of demand can be calculated as
Solution:
Following
information is given:
|
Q
= 50 units |
Q1=
60 units |
ΔQ =Q1-Q =60-50 =10 |
|
P
= ₹ 10 |
P1=
₹8 |
ΔP
= P1-P =8-10 = -2 |
|
Ed=? |
||
Note: (-) negative sign is prefixed to the formula
because price and demand are inversely related. Doing this would bring the
value of elasticity of demand to positive.
Interpretation:
The calculated value of
Elasticity of demand(Ed) is 1 indicates unitary elastic demand. It
implies that a 1% fall in the price of the commodity caused a 1% increase in its demand
showing that change in demand is equal to change in price.
2.
The quantity of a good demanded rises from 1 unit to 4 units when the price
falls from ₹4
to ₹ 2 per unit. The price
elasticity of demand for the good is approximately:
Solution:
Following
information is given:
|
Q
= 1 unit |
Q1=
4 units |
ΔQ =Q1-Q =4-1 =3 |
|
P
= ₹ 4 |
P1=
₹2 |
ΔP
= P1-P =2-4 = -2 |
|
Ed=? |
||
Note: (-) negative sign is prefixed to the formula
because price and demand are inversely related. Doing this would bring the
value of elasticity of demand to positive.
Interpretation:
The above calculated
value of Elasticity of demand(Ed) is 6 >1 indicates more than
unitary elastic demand. It implies that a 1% fall in the price of good causes 6%
increase in its demand showing that change in demand is greater than the change in
price.
3.
At ₹26 per unit, the demand for a commodity is 30 units. If the price increases
from ₹26 to ₹30 per unit, the demand decreases to 15 units. Calculate the price
elasticity of demand.
Solution:
Following
information is given:
|
Q
= 30 units |
Q1=
15 units |
ΔQ =Q1-Q =15-30 = -15 |
|
P
= ₹ 26 |
P1=
₹30 |
ΔP
= P1-P =30-26 = 4 |
|
Ed=? |
||
Note: (-) negative sign is prefixed to the formula
because price and demand are inversely related. Doing this would bring the
value of elasticity of demand to positive.
Interpretation:
The above calculated
value of Elasticity of demand(Ed) is 3.25 >1 indicates more than
unitary elastic demand. It implies that a 1% rise in the price of the commodity causes
3.25% fall in its demand showing that change in demand is greater than change
in price.
4.
When the price of a good falls from ₹10 to ₹8 per unit, its demand rises from
20 units to 24 units. What will be its price elasticity of demand?
Solution:
Following
information is given:
|
Q
= 20 units |
Q1=
24 units |
ΔQ =Q1-Q =24-20 = 4 |
|
P
= ₹ 10 |
P1=
₹8 |
ΔP
= P1-P =8-10 = -2 |
|
Ed=? |
||
Note: (-) negative sign is prefixed to the formula
because price and demand are inversely related. Doing this would bring the
value of elasticity of demand to positive.
Interpretation:
Thanks & please
Share with your friends
Comment if you have
any questions.
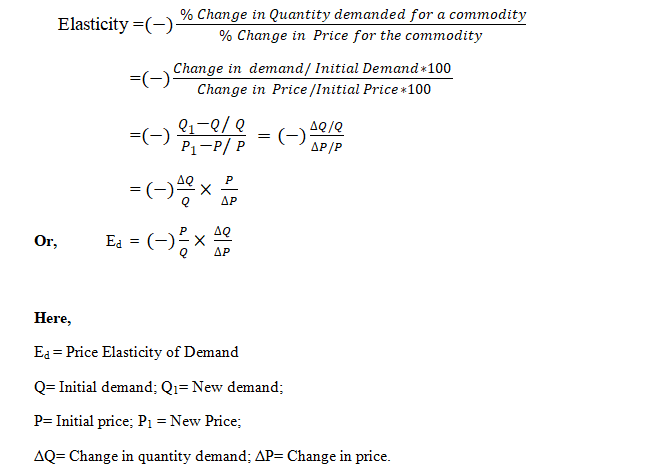

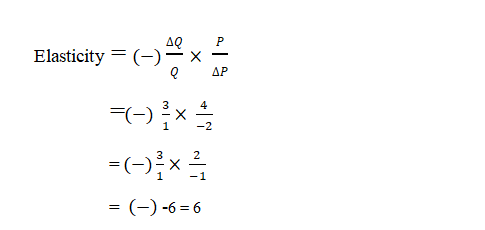





Comments
Post a Comment